
212-606-1408

Robotic Technology
Personalized Touch

Anterior Hip Replacement

Robotic Assisted
Knee Replacement

Partial Knee Replacement
Anterior Hip Replacement
Anterior total hip replacement is a surgical procedure designed to replace a worn or damaged hip joint. In this approach, the surgeon accesses the hip joint from the front (anterior) of the hip rather than the side or back. This method typically allows for less muscle and tissue disruption, which can result in a quicker recovery time and less postoperative pain compared to traditional hip replacement methods. During the surgery, the surgeon makes an incision at the front of the hip. The damaged bone and cartilage are then removed from the hip joint. This is replaced with artificial components: a metal or ceramic ball is placed on the top of the thigh bone (femur) and a smooth metal cup is fixed into the pelvis, replicating the function of the natural hip joint. The goal of this procedure is to relieve pain and improve mobility for patients suffering from severe hip arthritis or other hip-related problems.
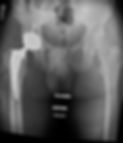

Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure aimed at relieving pain and restoring function in severely diseased knee joints. The surgery involves cutting away damaged bone and cartilage from the thigh bone (femur) and shinbone (tibia) and replacing it with an artificial joint made of metal alloys, high-grade plastics, and polymers. During the procedure, the surgeon makes an incision in the knee to expose the joint. The damaged portions of the femur and tibia are then precisely removed to fit the new metal components that replicate the surfaces of the joint. These components are typically cemented into place. A medical-grade plastic spacer is inserted between the metal components to create a smooth gliding surface. The primary goals of total knee replacement are to alleviate pain caused by joint degeneration due to osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or post-traumatic arthritis, and to enhance quality of life with improved movement and strength.
Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement, also known as unicompartmental knee replacement, is a surgical procedure intended for patients with arthritis limited to one compartment of the knee. Unlike total knee replacement that replaces the entire knee joint, partial knee replacement involves replacing only the damaged part of the knee, preserving as much of the natural knee as possible. During this procedure, the surgeon makes a smaller incision than in a total knee replacement. They then remove the damaged cartilage and bone from either the medial (inside), lateral (outside), or patellofemoral (front) compartment of the knee. The removed portions are replaced with metal and plastic components that mimic the natural movement and function of the knee joint. The advantages of a partial knee replacement include a more natural knee movement post-surgery, less bone removal, smaller incision, reduced blood loss, and often a shorter recovery time and hospital stay. This surgery is typically recommended for patients with limited knee arthritis who have maintained good range of motion and stable knee ligaments.


Robotic Joint Replacement
Robotic joint replacement is a technologically advanced surgical method used for performing joint replacement surgeries, such as hip and knee replacements. This approach utilizes robotic arms and computer-assisted technology to enhance the precision and accuracy of the procedure. In robotic joint replacement, the surgeon uses a robotic arm to assist with the surgery. Preoperative imaging, like CT scans, can be used to create a detailed 3D model of the patient's joint. This model aids the surgeon in planning the procedure with high accuracy. During the surgery, the robotic system provides real-time feedback and guides the surgeon in positioning the artificial joint components with enhanced precision. This technology allows for more exact placement and alignment of the joint prosthesis, which can potentially lead to better long-term outcomes, including increased implant longevity and improved function of the joint. It may also result in smaller incisions, less tissue damage, reduced pain, and faster recovery times compared to traditional joint replacement methods. However, the effectiveness and appropriateness of robotic joint replacement depend on individual patient factors and the surgeon's expertise.